These Timelines are a detailed look at the time and the influence of Cycles. Significant events of the decade are analyzed through Twelve categories that serve as a kaleidoscopic lens through time, (see the clickable links above), as well as the position of Cycles at the time, (see the clickable folder links in the upper left corner). You can read and link up and down vertically through this Timeline, or, you can go any Category and link horizontally to the same Category in other Timelines (links are provided at the head of each Category). This cross linking is designed to provide a fast and easy way to make reading fun and interesting.
See the go to Overview here link near the top for a brief look at Cycles for this decade.
See the Matrix links above left for navigating through all Overviews and Timelines by Time, Subject, or Cycle as described in Introduction to Part II).
Note to readers: Work from the Kala-Rhythm archives is being offered here in the Timelines for the first time. We are allowing a view into the Timelines now by posting both the finished and the unfinished pages of the Timelines as editing from our references continues. Unfinished pages (like this one) contain raw data from history sources to which we give credit in our "biblio/webography". Check back for updates to this and other pages.
WORLD WAR II: THE WAR YEARS
A time when a
social hypothalamus kicked in to respond to an emergency.
PRESIDENTIAL ELECTIONS
1940 FDR
re-elected Pres of the US for third term defeating Wendell
Willkie.
1944 R re-elected
for fourth term, w Truman VP.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1940 John L. Lewis,
anti-Roosevelt labor leader, resigns as head of CIO after election
1940 Congress
establishes the Fish and Wildlife Service to develop and administer a wildlife
conservation program.
1940 Congress
creates the Selective Service System, the first US peacetime program of
compulsory military service. It requires all men between ages 21 and 36 to
register.
1940 US Office of
Production Management for Defense is set up to coordinate work in defense
plants. It is authorized to send aid to countries fighting the Axis Powers.
1940 National
Defense Advisory Commission coordinates US civilian defense protection.
9/16/?? In addition
to increased funding for the the military that came earlier this year, Roosevelt
sings the Selective Training and Service Act *or Burke-Wadsworth Act), requiring
men between the ages of 21-35 to register for military training. Only the day
before, Canada had begun to call up men between the ages 21-24, and the USSR had
announced its intention to conscript young men aged 19-20.
11/5/40 In the
election, Roosevelt receives 27,244,160 pop votes to Willkie’s 22,305,198, and
takes 449 electoral college votes to Willkie’s 82.
1941 FDR wins third
term w 27 million, Willkie gains 22 million.
1941 Thousand join
the nation's industries that call for more workers; because of rising rents and
the unavailability of bldg, many are forced to live in tents an tarpaper cities,
raw-wood shacks, unused barns, garages, warehouses, and chicken coops.
4/25/45 Pres R
died in Warm Springs, GA, on the 83rd day of his fourth term; he was 63.
1945 Communist
Party was reestablished by the Communist Political Association, which voted to
disband itself.
1943 Pay-as-you-go
income tax system instituted in US.
WAR
1941 first peace
time draft begins.
1941 FDR Declares
state of "Limited National Emergency"
1941 After the
opening of the Russian front, the peacetime draft is accelerated; "Uncle Sam
Needs You" signs are posted in all public places.
1941 Pearl Harbor
statistic: 1,500 civilians killed, 1,500 inured; 5 battleships sunk or beached
(Arizona, Oklahoma, California, Nevada, West Virginia), 11 smaller ships
destroyed, 3 ships damaged so as to be unusable; 177 planes destroyed; 91 navy
officers killed, 20 wounded; 2,638 enlisted men dead, 636 wounded; 168 army men
killed, 223 wounded, 26 missing. TRIRHYTHMIC LOW
1942 Manila Falls,
MacArthur retreats to Bataan.
1942 War Production
Board is established / board stops all non-essential building
1942 WACS, WAVES,
APARS recruit.
1942 US government
transfers more than 100,000 Niseis (Japanese Americans) from West Coast to
inland camps.
1942 Gov wartime
agencies take control of housing, alien property, shipping and transportation,
foreign relief, censorship, and scientific research.
1942 Gen MacArthur
is made commander of Allied forces in Southwest Pacific.
1942 Congress
enacts measures forming Women's auxiliary corps of the Army, Navy, Marines, Air
Force, and Coast Guard
1942 Congress
lowers draft age to 18.
1942 FBI captures
German saboteurs brought by submarines to coasts of FL and Long Island, NY. 6
are executed and 2 imprisoned.
1942 400,000 Am
troops land in North Africa; Anglo-American forces take Tripoli and Tunis, the
Germans evacuate North Africa (May 1943).
1943 Gen Eisenhower
becomes Commander-in-Chief of all Allied forces in North Africa. US forces
capture Bizerte, Tunisia, and combine w the British to drive the Axis forces out
of Africa.
1943 US bombers
sink Japanese convoy of 22 ships at the Battle of Bismarck Sea.
1943 Burma declares
war on the US.
1943 US planes bomb
Rome and Rumania's Ploesti oilfields.
1942 Pres R repeals
Chinese Exclusion Acts.
1943 Am planes make
64,000 sorties and drop 55,000 tons of bombs during the year.
1943 The Am Jewish
Congress reports that over 3 million Jews have been killed by the Nazis.
1943 FDR and
Churchill meet at Casablanca and set goal of unconditional surrender
1943 Japanese
collapse on Guadalcanal.
1944 Congress
creates new rank, General of the Army ("five-star general"), for Generals
Eisenhower, Henry ("Hap") Arnold, MacArthur, and George C. Marshall.
1945 US armed
forces tot 7.2 million War casualties, 292,000 killed or missing, 613,611
wounded.
| 1. Political 1940s |
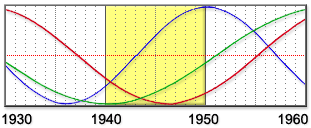
Physical Cycle |
top |
| |
Physical Low |
(1929 - 1943) |
10/17/41 The US destroyer
“Kearney” is torpedoed by a German U-Boat off Iceland; although the
destroyer does not sink, 11 Ams are killed. This attack comes only weeks
after the US Navy had announced its intention to protect all shipping as far
east as Iceland.
10/30/40 The US
destroyer “Reuben James,” on convoy duty off Iceland, is sunk by a German
U-Boat, with the loss of 100 Americans.
| |
Physical Upward Crossover |
(March 21, 1943 - March 21, 1944) |
8/1/43
Black Experience: A rumor of a murder in Harlem sparks a race riot that
ends w five people killed, 410 injured, and some $5,000,000 in damage.
| |
Physical High |
(1943 - 1957) |
1/16/44 Gen Dwight
Eisenhower arrives in London to take up the post of Sup Commander, Allied
Expeditionary Force, and lead what will become known as the crusade in
Europe to free the Continent from the German conquest.
3/6/44 With
some 800 fighter planes supporting them, 660 US bombers, make the first US
raid on Berlin. A second such raid will be made on march 8, and US losses
on both raids amount to some 10 percent. But these and the radicals that
follow almost daily on German cities will gradually weaken the Germans’ will
to resist.
6/6 44 D-Day
Operation Overlord, the invasion of the Continent, begins just after
midnight w the descent of two US airborne divisions, and in the early hours
of the morning with some 4000 invasion ships plus 600 warships, at least
10,000 planes (only one of which is shot down by the German Air Force) and
about 176,000 Allied troops. It is the largest such invasion force in
history, and the day itself is marked by both epic movements and statistics
and by individual acts of heroism. The landings take place along a series
of beaches in Normandy between Cherbourg and LeHavre, and although the
Germans have had some warning they have not concentrated on a unified
strategy.
6/10/44 The two
US beachhead armies - those from Omaha and Utah Beaches - link, and the
Allies forces are now ready to present a solid line to move against the
Germans. In effect, from this point on, and w many delays and a few
setbacks, the Allied forces will move inexorably eastward until Germany
surrenders in May 1945.
6/15/44 US
Super-fortresses, B-29s based on China, bomb Yawatta, the first such air
raid on a Japanese main island. In the Marianas, US forces land on Saipan;
by the time the island falls on July 9, the US will have suffered some 3400
dead, but the Japanese will have 27,000 dead.
8/10/44 The
island of Guan is retaken by US forces after some 20 days of fierce
fighting; the Japanese have lost some 17,000 men (w only 500 surrendering)
and the US have lost 1214 killed and some 6000 wounded, Guan had fallen to
the Japanese on Dec 13, 1941, so its recapture is of special significance to
the Allied cause.
9/12/44 The US
Army enter Germany for the first time, advancing only a few miles beyond the
border between Trier and Aachen.
1944 D-Day;
landing in Normandy June 6 (over 700 ships and 4,000 landing craft involved.
1944 US troops
establish beachheads at Utah Beach and Omaha Beach during Allied invasion of
Western Europe (D-day).
2/19 -
3/16/1945 one of hardest fought battles of entire war, US Marines capture
Pacific island of Iwo Jima, landing flat on Mount Suribachi creates image of
triumph that will become a symbol of fighting in Far East during WW II.
3/7/45 Remagen
Bridge over the Rhine R. was crossed by the US First Army. Not since the
days of Napoleon had an invading army crossed the Rhine.
3/16/45 Iwo
Jima fell to the US Marines after 35 days of bitter and bloody fighting.
More than 4,000 Marines were killed, 15,000 wounded. The Japanese last more
than 20,000 men.
4/1/45 Okinawa
was invaded by US forces.
5/8/45 On the
day, known as V-E Day, for victory in Europe, the instrument of
unconditional surrender was ratified in Berlin, ending the European phase of
World War II.
6/21/45 Jap
forces on Okinawa surrendered after two and a half months of deadly
struggle. More than 100,000 Jap soldiers were killed. Am deaths ran to
almost 13,000, w nearly 40,000 wounded.
7/5/45
Philippine Islands declared liberated by Gen Douglas MacArthur. In then
months of fighting since the first Am landings st Leyte, more than 400,000
Jap soldiers had been killed and upward of 12,000 Americans had lost their
lives.
7/16/45 First
atomic bomb was detonated near Alamogord, New Mexico, at 5:30 am.
1945 US drops
atomic bombs on Hiroshima Aug 6 and Nagasaki Aug 9.
4/24/45 The
United Nations conference opened San France. with delegates from 50 nations
attending. The UN charter was signed June 26. The United Nations charter
was ratified by the US Senate by a vote of 89 to 2.
8/6/45
Hiroshima Jap, was destroyed by the first atomic bomb to be used in war.
8/15/V-J Day,
for victory over Jap, marked the end of the Pacific phase of WW II.
9/2/45 formal
document of surrender signed aboard USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay.
5/7/45 The
world rejoices as the Germans surrender to the Allies at Rheims, France.
General Dwight D. Eisenhower accepts for the Allied forces.
6/21/45 After
some 25,000 Americans die and 160,000 Jap lose their lives, the Jap
surrender Okinawa to the US army.
8/6/45 The US
Air Force drops an atomic bomb on the city of Hiroshima, Jap. This is the
first application of atomic technology and the magnitude of destruction
astounds even those working on the Manhattan Project.
8/9/45
Nagasaki, Jap, is partly destroyed by a second atomic bomb. The US awaits
the response of the Jap government to this show of force.
| 1. Political 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 1. Political 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 1. Political 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
| |
Trirhythmic Low |
(1937 - 1943) |
The attack on Pearl Harbor
came as a surprise when were not ready. There was amazement at how we could
have been so open and unaware. This came while the intellectual cycle was at
the bottom.
DAT^
12/7/41 On
Sunday morning, 7:55 Honolulu time, Jap bombers attack Peal Harbor, the
major US naval base in Hawaii. Nineteen US ships *including 6 battleships)
are sunk or disable; some 150 planes are destroyed; 2403 soldiers, sailor
and civilians are killed, 1178 are wounded. Other Japanese planes and ships
attack US bases in the Philippines, Guan and Midway, as well as British
bases in Hong Kong and the Malay Peninsula.
1/26/42 The
commission that has been investigating the disaster at Pearl Harbor releases
its finding. Both Gen Short, then commander of the Army’s Hawaiian
department, and Admiral Kimmel, then commander in chief of the US fleet in
the Pacific, are found to have been guilty of dereliction of duty. But both
have already been dismissed from active duty, and the debate over the
responsibility and blame for decisions taken or not taken will in fact never
completely cease. Even 40 years later, historians and researchers will be
writing to assign blame, some actually claiming that Roosevelt knew details
of the imminent attack far enough in advance to warn the military but chose
not to in order to force the US in to the war. But there is never any solid
evidence of the such literal foreknowledge; what does seem apparent in the
years that follow is that many men running the US government and limitary
were derelict in their duty.
12/8/41 Pres R
appears before a special joint session of Congress an, declaring December 7
“a day that shall live in infamy,” asks that the US declare war against
Japan. The Senate votes to approve 82-0, the House of reps 388-1 (the lone
dissenter being the pacifist Jeanette Rankin, the first woman elected a Rep
and who also voted against the US entering the war in 1917). With this
formal declaration of war, Pres R begins to direct every branch of the US
military and government toward this one effort.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1940 DJIA high 152, low 113
GNP +10% inflation +).4% unemployment 14.6%
1940 unemployment:
8,120,000 GNP: $99.7 billion fed budget: $13.2 billion national debt:
$43.0 billion prime rate: 0.6% CPI (1967 = 100): 42
1940 US GNP 100.6
(up 1-% from 1939);
6/25/40 The Fair
Employment Practices Committee is established by executive order to prevent
discrimination due to race, creed or color in defense-related work.
1943 US Supreme
Court rules that children need not salute flag in schools if it is against their
religion, in case brought by Jehovah's Witnesses.
1944 World Bank is
created at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, conference.
Outside the USA
and transport, coal remained the dominant source of power in this period; as
late as 1940, three-quarters of the world's energy was provided by coal and less
than 20% by oil.
RAW^
1941 Off of Price
Administration and Civilian Supply is set up. It immediately freezes steel
prices and later announces tire rationing to conserve rubber.
1941 John L. Lewis
threaten coal strike, FDR intervenes.
1941 U.S. Declares
war on Japan, Germany and Italy declare war on US., US declares war on Germany
and Japan.
1941 US Office of
Price Administration (OPA) established to regulate prices w Leon Henderson as
its head: OPA freezes price of steel; rubber rationing instituted.
1941 US Savings
Bonds and Stamps go on sale.
1941 draft is
extended, men 18-65 must register, those 20-44 may serve.
1941 $10 billion is
appropriated for defense.
1941 With the
shortage of certain metals, use of plastics increases; Philip Wrigley, ingum
packaging, introduces cellophane in place of tinfoil; Lucky Strike substitutes a
white and red bull's-eye logo for its green and red one, since green ink
contains metal.
1941 W the
improvement in the economy, car sales soar; alcohol consumption also rises.
1941 Henry Ford,
for the first time, agrees to negotiate w a union.
1941 Chrysler
begins builds the M-3 tank; GM, the B-25 bomber; Fore, Pratt Whitney engines.
1942 The OPA stops
all car and truck production; sug, tire and gas rationing beings.
1942 Boy Scouts
savage 150,000 tons of wastepaper; children receive 50 cents a pound per
aluminum foil ball.
1941 US Supreme
Court upholds Federal Wage and Hour Law restricting work of 16 and 18 year olds
and setting minimum wage for businesses engage in interstate commerce.
1942 On billion
pounds of plastics are produced for use in everything from airplanes to hose
nozzles; metal is replaced in every possible way.
1942 Rationing of
foods and materials needed for the war effort begins; sugar, coffee, fuel oil,
gasoline, butter, meats, cheese, canned foods, and finally, shoes are rationed.
| 2. Business & Economy 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| |
Physical Upward Crossover |
(March 21, 1943- March 21, 1944) |
1943 As blacks move into
the Detroit plants, racial tensions heighten; a riot develops when a black
is killed for using a white swimming area. [what mo.?]
1943 Race riots
break out in several major US cities whose labor population has been
bolstered by influx of southern Blacks. [what mo.?
6/20-22/43
Black Experience: Whites protesting the employment of of blacks in Detroit,
Michigan, clash w blacks and before Federal troops can put down the ensuing
riot and rampage, 34 people are dead.
12/27/43 The
Fed Gov seizes the nation’s railroads threatened w a shutdown by striking
workers.
| |
Physical High |
(1943 - 1957 |
9/45 Pre T issues exec
order proclaiming fed authority over all national resources beyond the
continental shelf.
1943 Despite
the 28-ounce allowance per week, meat consumption rises to 128.9 pounds per
year.
1943 With the
combined goods scarcity and improved economy, long lines develop at
groceries, movies, bars, and restaurants; cabs are obliged to take as many
passengers as they can carry; long-distance calls are limited to five
minutes.
1943 The
manpower shortage stimulates "pampering" of employees; music is piped into
factories, and coffee breaks and suggestion boxes are instituted, as well as
awards and fringe benefits. FDR orders a minimum 48-hour work week in war
plants.
1944 With 3.5
million women working alongside 6 million men on assembly lines, production
capacities change. Cargo ships are completed in 17 days, bombers in 13 days,
For the working woman, slacks becomes, as Max Lerner puts it, a "badge of
honor."
1944 Nearly
half the steel, tin, and paper needed for the war are provided by people
salvaging goods.
1945 Women auto
workers in Detroit, laid off because of returning war veterans, stage a
march w posters such as "Stop Discrimination because of Sex."
1945 Moving to
restore the civilian econ, Pres T ordered full restoration of civilian
consumer prod and collective bargaining, and a return of free markets.
1945 Rationing
ends for most goods.
8/45 Gen
MacArthur named Supreme Commander of Allied Powers in Japan.
| 2. Business & Economy 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 2. Business & Economy 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 2. Business & Economy 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
| |
Physo-Intellectual
Low - Rising |
(1940 1950) |
1940
McDonald's is started by Pasadena movie owners Richard and Maurice McDonald.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
The significant development of
the nuclear age was the explosion of the first atomic bomb. The Manhattan
Project developed this in the Fourth Quarter of the Intellectual Cycle, not the
First, (thought there was a Physical First Quarter). This was an emergency
development in response to World War II, and external development. Not all
developments, therefore, are limited to cyclical stages.
DAT^
An an
estimated 30,000,000 US homes now have radios.
WAR
1943 First nuclear
reactor established at Chicago U.
1943 First
automatic computer dev in the USA
1943 magnetic
recording tape dev [what country?]
1944 first atomic
bomb, code-named "Trinity," exploded near Alamogordo, New Mexico Three weeks
latter, a U-235 atomic bomb (equal to 20,000 tons of TNT) is dropped on
Hiroshima, Japan. Three days after this, a plutonium gassed A-bomb is dropped on
Nagasaki, Japan. Bothe cities are destroyed and more than 130,000 people are
dead or missing as a result of the most powerful weapons ever used in a war.
1945 Aside fr the
war victory, the biggest news of the year was the use of atomic energy.
Scientists questioned the moral and ethical value of their contribution to
victory in the war. At first , the pub refused to share the alarm of the
physicists, believing that the people who had created this new force would soon
tell the world how to control it. Unfortunately, this did not come to pass.
1940 First electron
microscope demonstrated by Radio Corporation of America, Camden, NJ.
1940 V. Zworykin
and James Hillier invent the electron microscope.
1941 Bush heads the
newly-formed Office of Scientific Research and Development.
1942 The first
electronic brain or automatic computer developed in the US.
1942 magnetic
recording tape invented.
1942 The first safe
self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction is accomplished by Enrico Fermi, Edward
Teller, and Leo Szilard, at the U of Chicago.
1945 The first
atomic bomb exploded in the Alamogordo, New Mexico, desert is a plutonium bomb;
its power (equal to 20,000 tons of TNT) exceeds expectations.
1945 F. Block,
William Hansen, and Martin Packard devise the principle of nuclear magnetic
resonance (nuclear inductions).
1945 After months
of secret research, atomic scientists see results of efforts on the Manhattan
Project; detonation of first atomic bomb at Alamogordo, New Mexico. Among
contributors are J. Robert Oppenheimer, in charge of weapons laboratory at Los
Alamos.
1945 Langmuir
experiments with cloud-seeding, using chemicals such as silver iodide or sold
carbon dioxide (dry ice) to cause rain or snow artificially.
1945 Vitamin A is
synthesized.
1945 RCA's new
camera, the image orthicon, has 100 times the sensitivity of the previous
camera, dev in the 1920s.
1942 tubeless tires
are successfully tested.
1942 Magnetic
recording tape is introduced.
In the 1940s
several different antibiotics were discovered, including streptomycin, which is
particularly useful in controlling whooping cough and stomach aches.
1940 New combustion
chamber for jet engines designed [AM?}
1941 Louis Fielse,
at Harvard, develops napalm, a jellylike mixture of gasoline and palm oils that
sticks to its target until it burns out.
1941 "Manhattan
Project" of intensive atomic research begins.
1942 Erico Fermi
(US) splits the atom.
1942 Bell Aircraft
tests first US jet plane.
1942 Bazookas,
shoulder-held rocket containers used as antitank weapons, are dev.
1942 Radar comes
into operational use.
1942 A
jet-propelled plane is tested by Bell Aircraft.
Jets 1st tested un
US 1942. In June 1944 a Lockheed P-80 propelled fighters were ordered by US Air
Force (1947);
1943 Penicillin
successfully used in the treatment of chronic diseases [Am?]
1943 US War Labor
Board orders coal mines to be taken over by the government when 0.5 million
miners strike.
1943 Selma Waksman
discovers streptomycin and coins the term "antibiotic: for the actinomycete
streptomyces griseus.
1943 Sulfa is
credited w an extraordinary reduction of US Army fatalities.
1943 The tiny town
of Oak Ridge, Tennessee, is suddenly populated by 50,000 scientists and aides,
all conducting secret atomic research.
1943 Oppenheiner
organizes the Manhattan Projects' top-secret Weapons Lab in Los Alamos, New
Mexico.
1944 Howard Aiken,
mathematician, invents the "Mark I," an automatic calculator that is the
forerunner of the digital computers.
1944 A mathematical
"robot," a giant, automatic, sequence-controlled computer with a 50-foot panel
of knobs, gears, and switches, is created at Harvard by Howard Aiken and IBM
engineers.
RAW^
In 1944 Harvard
University engineering professor Howard Aiken develops the first digital
computer, the operation of which was controlled by mechanical and electrical
apparatus. Two years later research engineers at the University of ?? made the
first totally electronic digital computer, whose circuits were controlled by
vacuum tubes.
RAW^
1944 DNA, the basic
material of heredity, is isolated by Oswald Avery, Rockefeller Institute.
| 3. Science & Technology 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| |
Physical 1st Qtr. Foundation |
(1943 - 1950) |
1943 DDT is introduced in
the US and hailed as a boon to farmers.
1943
Large-scale production of penicillin begins to meet the demand as the drug
is being used to treat a variety of infectious diseases.
1943
Polyethylene plastic is introduced.
1945 The navy
reports a "complete cure" for cholera.
1945 Dr.
William Robbins reports the dev of six new antibiotics; pleurotin, grisic
acid, pleurin, irpexin, obtusin, and corticin; streptomycin, corticin, and
pleurotin are marketed.
1945
Penicillin, previously distributed to the armed forces, becomes more
available to the civilian pop.
| 3. Science & Technology 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 3. Science & Technology 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 3. Science & Technology 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1940 First successful
helicopter flight in US by Vought-Sikorsky Corporation.
1942 Henry J.
Kaiser industrialist, develops techniques for building 10,000-ton Liberty Ships
in four days. First ones launched in 1943.
| 4. Mechanical 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| |
Physical 1st Qtr. Foundation |
(1943 - 1950) |
1942-45 Rocket in World War
II. "Bazooka," 1st US rocket fun, dev by Capt. L. A. Skinner and C. N.
Kickman; standardized, 1942. Germans 1st used V-1, 250-400-mph pilot-less
aircraft, 12 June 1944, 6 days after D-Day; shot down by Allied gunners
aided by radar, M-9 director, and proximity fuse. V-2 (long-range rocket,
3.4000 mph) began to land in London on 12 Sept. 1944. Rocket and
guided-missile experiments pushed in postwar period US Navy guided missiles
reported used in combat in Korea (1 Sept, 1952).
1942-60 Jet
Planes. Jet engine 1st produced by Brit inventor, Frank Whittle, 1937. Jets
1st tested un US 1942. In June 1944 a Lockheed P-80 propelled fighters were
ordered by US Air Force (1947); bombers dev (1947). By 1952, US had dev B-52
bomber, with 8 turbojet engines, ceiling 50,000 ft., speed c. 600 mph.;
B-47, c. 700 mph. B-70 supersonic heavy bomber (designed for speeds
exceeding 2,000 mph) program drastically restricted by gavt. 1 Dec. 1959.
Bell X-2 rocket-powered research airplane set speed record in excess of
2,100 mph (1956); North American X-15 rocket plane made 1st successful
flight under own power 17 Sept. 1959. Commercial jet transport initiated 15
Aug. 1958 w Boeing 707 (transatlantic service by Pan American Airways, 26
Oct. 1958), followed by Douglas DC-8 (1959), and Convair 880 (TWA, 1961).
1943 Kaiser
develops techniques of pre-fabrication that allow him to build a 100,000-ton
"Liberty ship in 4 days.
1944 Theodore
Von Karman, "Father of the Supersonic Age," helps establish the Jet
Propulsion Laboratory in CA.
1944 The US
Army announces the dev of a jet-propelled, prop-less plane.
1941 Yale,
Harvard, and Princeton decide to cut their programs from four to three years
by staying in session all year round.
| 4. Mechanical 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 4. Mechanical 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 4. Mechanical 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
| 5. Education 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| 5. Education 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 5. Education 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| |
Intellectual Low |
(1929 - 1951) |
12/29/40 Illiteracy in the US has reached a new low of 4.2 percent (down
from 15.8 percent in 1870).
| |
Intellectual XXXward Crossover |
(March 21, 1000- March 21, 1000) |
ZZZ 5. EDUCATION INTELLECTUAL CROSSOVER DATA
| 5. Education 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
Perhaps
it was the concomitant anxieties of World War II and the Cold War that
influenced many Americans to recommit themselves to organized religion from 1940
to 1960, membership in churches and synagogues increased substantially. One
manifestation of the surge in religious awakening was a tide of revivalism.
| 6. Religion & Spirituality 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| 6. Religion & Spirituality 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 6. Religion & Spirituality 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 6. Religion & Spirituality 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1943 US Army engineers complete
the Pentagon bldg. This 5-sided bldg, headquarters of the Dept of Def, remains
the largest office bldg in the world.
1943 Transportation
difficulties created by the war curtail international exhibitions, w a resulting
emphasis in the US on native art and patriotic themes.
| 7. Arts & Design 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| 7. Arts & Design 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 7. Arts & Design 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 7. Arts & Design 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
| |
Trirhythmic string of
4th Qtr. Alternatives |
(1936 - 1955) |
During the mid-1940s and
the 1950s many Am painters turned from social criticism to a new movement
called abstract expressionism. The traditional subject matter of painting,
such as the human body, still life, or a rural scene, was lf little or no
concern. Within a basic structure of nonrepresentational internet, the focus
was upon such things as the utilization of space, of dimension ( a huge
canvas was often preferred), of surface textures of colors. Abstract
expressionism was the first major movement in American pointing whose
practitioners emphatically declined to imitate a European style. Indeed, the
abstract expressionists affected the trend of painting outside the US,
exerting such influence that the painting center of the world shifted from
Paris to NYC.
Painters like
Jackson Pollock, Willem de Kooning, and Arshile Gorky worked in the new form
of abstract expressionism. The music world saw the debuts of Leonard
Bernstein, Richard Tucker, Jan Peerce, and Lorin Maazel (age 11), and
premiers of Paul Hindemith, Bela Bartal, Arnold Schoenberg, and Igor
Stravinsky, all now residing in the United States.
RAW^
The first film
of experimentalist Orson Welles, was "Citizen Kane" (1941), which is
considered by virtually all critics one of the very greatest motion pictures
ever made. The film was loosely based on the life or newspaper publisher
William Randolph Hearst.
1940 First
large-scale urban college bldg. of modern design, Hunter College, is built
in NYC.
1940 Important
abstract expressionist painters of the time include Lore MacIcer, Morris
Graves, and Hans Hofmann.
1941 Orson
Welles directs and stars in "Citizen Kane," a film which introduces many new
techniques.
1941
"Doomsday," a painting by impressionist Karl Knaths, shows Cubist
influences.
1943 Robert
Motherwell, painter, brings abstract expressionism in a new direction w his
most famous work, "Pancho Villa, Dead and Alive."
1943 Jackson
Pollock's first one-man show
1943 Jackson
Pollock, "Pasiphae," "Search for a Symbol," "The She-Wolf."
1943
"Pharmacy," a work by assemblage sculptor Joseph Cornell, incorporates
mirrors to give unusual effects.
1943 Frank
Lloyd Wright: Southern College, Lakeland, Fla.
1944 Arshile
Gorky, "Water of the Flowery Mill." Oil painting of abstract style, at the
Metropolitan Museum of Art. [Am?]
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
Book publishing had a boom
year, 1945, with the paperback trade continuing to create hundreds of thousands
of book buyers.
1940 bestseller,
"The Grapes of Wrath," John Steinbeck / "You Can't Go Home Again," Thomas Wolfe
(posthumous)
1940 Eugene
O'Neill: "Long Day's Journey into Night" / Ernest Hemingway: "For Whom the Bell
Tolls" (his most famous work) / Upton Sinclair: "World's End," first of the
Lanny Budd novels.
1940 Carl Sandburg:
"Abraham Lincoln: The War Years," Pulitzer Prize history.
1941 Upton
Sinclair, "Between Two Worlds"
1941 Howard Fast,
novelist, pubs "The Last Frontier," a historical novel about the mistreatment of
the Indians.
1942 C. S. Lewis
"The Screwtape Letters"
1944 Paper
shortages stimulate publishers' experiments w soft-cover books.
1944 Boston bans
"Forever Amber: and "Strange Fruit," the latter about the love between a white
man and black woman.
1944 Tennessee
Williams, "The Glass Menagerie," his first successful work.
| 8. Literature & Publication 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| 8. Literature & Publication 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 8. Literature & Publication 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 8. Literature & Publication 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
Betty Grable and Rita
Hayworth were the sex symbols of the early decade, and their pinups were GI
favorites;
DAT^
By the end of the
twenties there were some 13 million radios in American homes. The first
broadcasting station had opened in Pittsburgh in 1920; by 1940 there were nearly
900 radio stations and 52 million sets in use.
RAW^
1940 Nickel
jukeboxes appear in taverns, tearooms, variety store, gas stations, restaurants,
and barber shops. The popular Lindy Hop generates Saturday night social clubs;
new dances including La Varsonviana; the rhumba peals in popularity; Arthur
Murray creates the "Americonga" and "Rhumba Reel."
RAW^
First drive in
theater built in New Jersey, 1941? (December?)
1941 FCC authorizes
TV broadcasting. By the end of the year, 1 million sets are sold.
1942 The US becomes
the world music center and shelter for foreign musicians.
1942 Othello, with
Paul Robeson and Uta Hagen, has the longest Broadway run of any Shakespeare play
to date.
| 9. Entertainment 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| |
Physical High |
(1943 - 1957) |
In the 1940s a
revolution in American musical theater was effect by the team of Rodgers and
Hammerstein. In their first show together, "Oklahoma!, (1943)" which starred
Alfred Drake, features the unforgettable songs "Oh, What a Beautiful Mornin',"
"The Surrey with the Fringe on Top" and People Will Say We're in Love." In
her contribution to "Oklahoma!" ballet choreographer Agnes de Mille not only
revolutionized the style of dance in musicals but also, in using dance to
advance the plot, played a significant role in bringing about a basic change
in musical theater itself.
During the
1940s Country and Western music began to attract nationwide attention. The
growing popularity was due in large part to the talent of singer Jimmie
Rodgers.
1941 W soaring box
office receipts Hollywood can barely produce films fast enough, and many
westerns and grade B and C films are released.
RAW^
| |
Physical 1st Qtr. Foundation |
(1943 - 1950) |
1943 Rodgers and
Hammerstein: "Oklahoma!," musical play, New York (reached 2,248 consecutive
performances), special Pulitzer Prize (1944).
1943 Jitterbug
is the most popular dance. As part of the dance the man swings his partner
over his back and between his legs.
1943 The
musical “Oklahoma,” by Richard Rodgers and Oscar Hammerstein, opens on
Broadway and becomes an immediate and long-running popular and critical hit;
it also stands as a milestone in Merinda musical theater by leading musical
away fr show business glitter and into more indigenous American subjects.
Hollywood
retained its rep for making the world's best motion picture musicals. some
the most tastefully crafted among this type were "Meet Me in St. Louis"
(1944).
1945 Hollywood,
hungry for plots, was willing to pay as much as $250,000 for rights to a
good story. W such prizes before them, writers tailored their techniques to
fit the requirements of the screen. The result, by an large, was
undistinguished. By war's end, the Hollywood Victory Committee had arraigned
for 55,619 personal appearances of movie stars at bond rallies and military
camps.
1945 Many
families take their first vacations since Pearl Harbor; cabaret shows open
in cities like Las Vegas, a by-product, in part, of the USO troop shows;
motel construction increases.
1945 Dizzy
Gillespie tours w his first big band. Bop is at its peak. Miles Davis goes
to NY to study at Julliard. June Christy joins Stan Kenton; Charlie Shavers
joins Tommy Dorsey.
1945 Frank
Sinatra earns $13,5000 a week, almost $1 million a year.
| 9. Entertainment 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| |
Emotional 3rd Qtr. Review |
(1937 - 1946) |
1940
Disney's "Fantasia," an animated expression of classical music, features
Stokowski conducting the Philadelphia Orchestra. (unsuccessful).
1942 80 war
movies are made.
1942
"Casablanca" made w Humphrey Bogart and Ingrid Bergman
Among the
great movies of the decade - and perhaps of all time - were "Citizen Kane,"
(1941) , "The Grapes of Wrath," (1940) (for which dir. John Ford won an
Oscar), and "Casablanca," (1942) as well as the revival favorites "The
Maltese Falcon," and "Mildred Pierce." Many patriotic war movies appeared,
such as "Mrs Miniver," "The Purple Heart," and "Guadalcanal Diary."
DAT^
| 9. Entertainment 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 9. Entertainment 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
1943 Dance tempos are
either very fast of slow, for the fox trot, polka, rhumba, samba, waltz,
jitterbug, and Lindy hop, along with their variations, the Jersey jump, flea
hop, job walk, victory walk, and "Praise the Lord and Pass the Ammunition"
dance
| |
Trirhythmic string of
4th Qtr. Alternatives |
(1936 - 1955) |
Music, which represents all
the cycles, had heavy fourth quarter influence in the 1940s from the
physical cycle (1936-1943), the emotional cycle (1946-1955), and the
intellectual cycle (1940-1951). It was in this time period that one of the
most striking examples of experimental and abstract forms of American music
was developed, Progressive Jazz, also known as cool jazz. The 1949
recordings of Miles Davis marked its arrival.
DAT^
1940 Duke
Ellington becomes known as composer and jazz pianist.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1944 Many retired major
leaguers return to active play, since many young players are now in the service.
1940 "Students derive no special benefit from intercollegiate football," says
the U of Chicago, as it withdraws fromthe Big Ten.
1941 "Gentleman" Joe Louis, who
defeats a contender a month, becomes a national hero.
RAW^
| 10. Sports 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| |
Physical High |
(1943 - 1957) |
1944 Maurice Richard
(Montreal Canadians) scores a record 50 goals in the 50-game season.
Sports
attendance soared beyond 1920s levels. In football, the T-formation,
validated by Sid Luckman in Chicago's 73-0 victory against Washington
(1940), moved into prominence.
| |
Physical 1st Qtr. Foundation |
(1943 - 1950) |
1943 because of the war,
spring training is held in the North for the first time.
| 10. Sports 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 10. Sports 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 10. Sports 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1940 "air force blue" becomes
popular Suit lapels are decorated with enamel shields in all colors; eagles
appear on hatbands and purses. The times demand an emphasis on simplicity,
economy, and practicality; short dresses, simple suits w pleated skirts; day
dresses that can be worn at night w a muff or fur. New fashions including day
dresses with aprons and pinafores and, at the other extreme, with aprons and
pinafores and, at the other extreme, South Sea sarons (after Dorothy Lamour) in
colorful slinky crepes that expose the bare midriff and uplift bosom. Hair is
worn to the shoulder with big curls, piles on top of the head with curls and
pompadour. or curls into a sausage in the back. Lips are modeled like Crawford's
"Bow tie," in shades like "Regimented Red" (with matching polish); powder and
rouge are applied over pancake makeup.
For men: Fashion
are marked by anew conservatism; the granite gray or blue striped suit; solid or
red, blue, and white striped ties worn in Windsor knots; and spread-collared
white, blue, or blur-white striped shirts. Rayon is introduced for wrinkle-proof
ties.
RAW^
1941 government
regulations call for austerity in the use of fabric in making clothes.
DAT^
1942 Sales or
women's trousers are five to ten times greater than last year.
1943 Two silhouette
predominate: the slim, tubular look in knitted dresses or chemises with cinche
belts, and the bulky look in box suits and coasts with heavy, loose fabrics.
Hair is neat, folded at the ear, netted at the back, twisted into braids, or
pinned on top of the head. Small tight hats and snoods remain fashionable.
Later, the "versatile suit," snipped-in waist, short jacket, back hiked or
pleated skirt, is popular. Woman wear suits everywhere. Coarse arlon (the
"officer's" style), or short (the "seaman's"). The fur-lined wool or canvas
coast is new. Lounging teenage girls wear rolled-up jeans, sloppy shirttails,
mixed shoes, and rag curlers. for men: Male teens are offered the "zoot suit,"
a long, one-button jacket w large padded shoulders, peaked lapels, and high-waisted
trousers ballooning at the knees and gripping at the ankles, worn w knee-length
key chains, broad-brimmed hats, and wide silk ties against striped or colored
shirts. (Popular with "hep cats"). Older men reject mustaches because of their
current, fascist associations.
1943 Shoes are
rationed a 3 pairs a year; new sneakers are unavailable because of the rubber
shortage.
1944 W fabric still
limited, three-quarter-length box coats and suits have false fronts; sleeveless
dresses expose wide shoulders or have small shoulder caps. Chignons, as well as
small pillbox hats and berets, draw attention to the face and makeup; the
earring industry expands. Décolletage returns for birth day and evening wear.
The concept of "separates," or interchangeable clothes, enters the fashion
world. For men: War Production Board specifications, since 1942: 23 3/4" length
for size 37 jacket; no waistcoat; trousers 22" at the knee, 18 1/2" at the
bottom, 35" inseam for 32" waist; no cuffs, pleats, tucks, or overlapping
waistbands.
RAW^
1945 Cropped
jeans and pants w stockings in the same rib (foreshadowing tights) are shown.
| 11. Fashion 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| 11. Fashion 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 11. Fashion 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 11. Fashion 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
1940 pop 132 million (7.3%
increase since 1930 - smallest increase since statistics were begun in 1790),
including 0.5 million immigrants, mostly European refugees; Alien Registration
Act show presence in US of 5 million aliens; farm 23.3%
More than 56% of people live in
places of 2500 or more population. 1940 average life expectancy in US 64 (
from 49 in 1900) 1940 life expectancy male 60.8 female 68.2 births/1,000
19.4 marriages/1,000 12.1 divorces/1,000 2.0 deaths/1,000 12.1
1940 Oglethorpe U.
(GA) deposits a bottle of beer, an encyclopedia, and a movie fan magazine along
w thousand of other objects in its "Crypt of Civilization," a time capsule not
to be opened until the year 8113.
1941 A 6-ton
granite monument over the site of time capsule is unveiled in Flushing Meadow,
Queens, NY. A souvenir of the NY World's Fair, capsule contains artifacts and
info about 20th-century culture to be recovered in the year 6939.
1943 Friday's
become "meatless days"; casseroles, fish, omelets, and soufflés becomes popular.
1943 With the paper
shortage, few Xmas cards are available; women recycle their brown grocery bags.
1944 "Kilroy was
here" graffiti moves out of pub bathrooms to billboards, buildings, phone
booths, and construction fences, mythologizing the valor of the GI.
1944 Richard Bong,
25, surpasses Eddie Rickenbacker's 26-year-old record by destroying his 27th
Japanese aircraft.
1944 Major
hurricane w winds up to 134 mph strikes the Atlantic coast from Cape Hatteras,
NC, to Canada, killing 390 at sea and about 50 on land. Damage estimate at $50
million.
1945 The shortage
of an estimate 4,660,000 homes forces many into makeshift arrangements that
range from "doubling up" to living in autos.
| 12. Lifestyles 1940s |
Physical Cycle |
top |
| 12. Lifestyles 1940s |
Emotional Cycle |
top |
| 12. Lifestyles 1940s |
Intellectual Cycle |
top |
| 12. Lifestyles 1940s |
Polyrhythms |
top |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| top |
 drop down to navigate category in other decades: drop down to navigate category in other decades:  |
|
|
|
| |
...
============
top
|
|
 Kala. Chart horizontal
Kala. Chart horizontal





 1930s
1930s